Solve problem
Overview
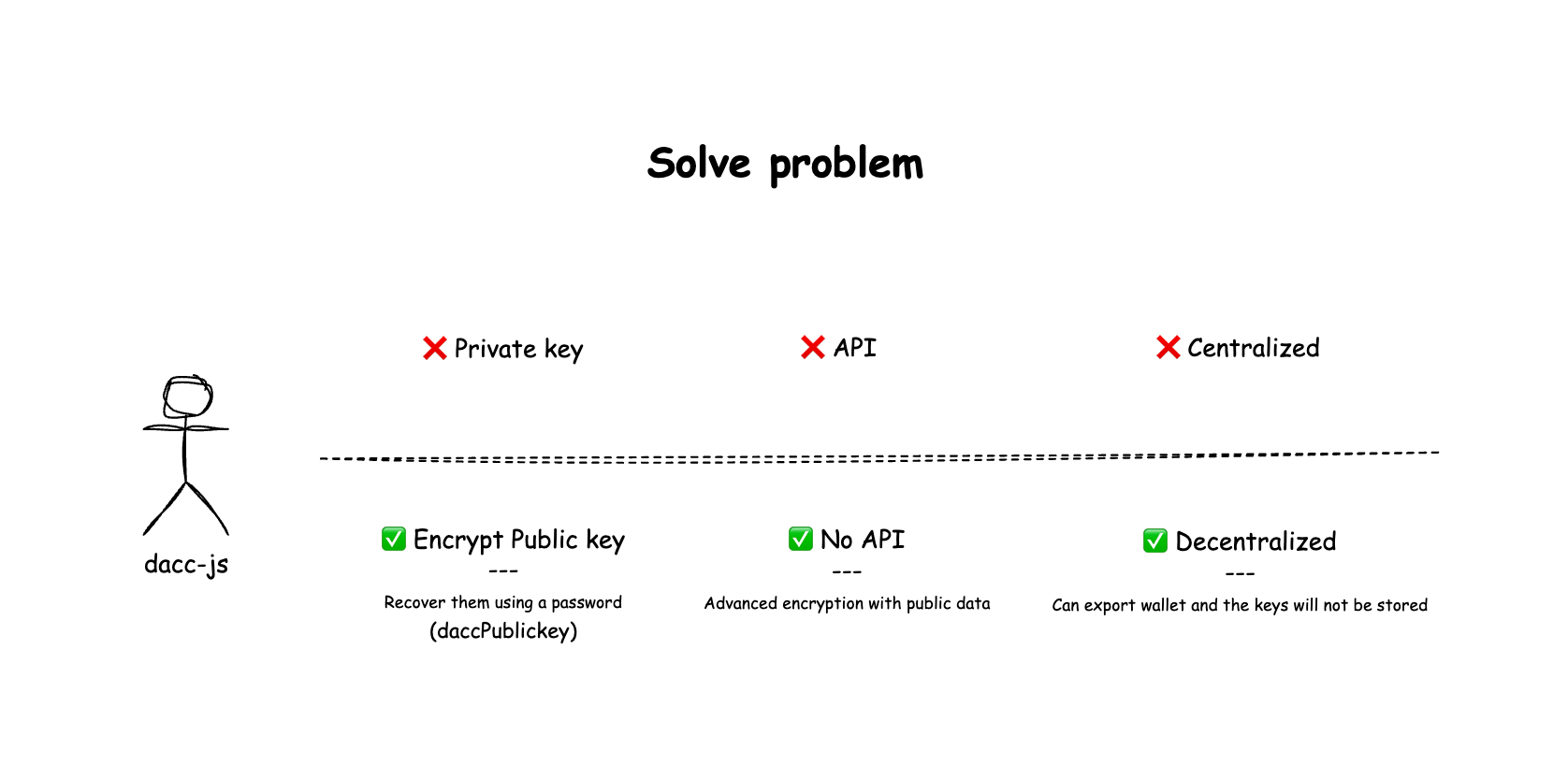
This diagram illustrates the Core Philosophy driving the design of the dacc-js library. The primary goal is to resolve fundamental issues often found in traditional Web3 wallets for Web2 solutions and services: reliance on intermediaries and data centralization.
Solved model
dacc-js is engineered to eliminate the limitations and security concerns arising from dependency on external services when accessing your account directly.
| Type | The Old Problem | The Dacc-js (Solution) |
|---|---|---|
| Key | ❌ Private Key | ✅ Encrypt Public key (daccPublickey) |
| Service | ❌ API Dependent | ✅ No API Dependency |
| Data | ❌ Centralized | ✅ Decentralized |
Key
Problem: Private Key
Traditional wallets require users to directly handle raw private keys, creating significant security and usability challenges:
- Complex Format: Managing long hexadecimal strings (64 characters) is error-prone and intimidating for users.
- Storage Risk: Private keys stored in plain text files or screenshots are vulnerable to theft or accidental exposure.
- Recovery Difficulty: Lost private keys mean permanent loss of assets with no recovery mechanism.
- Human Error: Easy to copy incorrectly, share accidentally, or store insecurely.
Solution: Dacc-js - Encrypt Public key (daccPublickey)
dacc-js transforms wallet security by using encrypted public keys instead of exposing private keys, while enabling password-based recovery:
- Familiar Interface: Users work with passwords they already understand and trust for key recovery.
- Strong Encryption: Private keys are never exposed - only encrypted public keys are handled.
- Password Recovery: Private keys can be recovered using your password without storing the actual private key.
- Better UX: No need to manage complex hexadecimal strings or worry about private key exposure.
Enhanced Security: Your private key can be recovered from your password and encrypted public key, but the private key itself is never stored or transmitted. Even
dacc-jscannot access your private keys without your password.
Service
Problem: API Dependent
Most wallet services often rely on a specific provider's API for sending commands, checking status, or even partial key management:
- Single Point of Failure (SPOF): If the API goes down, the service is interrupted.
- Censorship Risk: The service provider can potentially block or restrict your access.
Solution: Dacc-js - No API Dependency
dacc-js is built to integrate directly with robust, standard Web3 libraries like ethers and viem, as well as other developer tools.
By utilizing: these libraries all transactions are handled Peer-to-Peer or by directly connecting to a blockchain node. This means you are permissionless and do not require authorization from any intermediary to use your wallet.
Data
Problem: Centralized
In a centralized system, critical data like Private Keys might be stored on a company's servers (even if claimed to be encrypted). This introduces risks:
- Data Breach: If the server is compromised, stored Private Keys are at risk of leakage.
- Lack of Control: You do not have absolute, sovereign control over your keys.
Solution: Dacc-js - Decentralized
dacc-js adheres strictly to decentralized principles:
- No Key Storage: The system does not store your unencrypted private keys on any server.
- Export Capability: Users can export their wallet and independently manage of their encrypted data.
The Result:
dacc-jsreturns control of the wallet to the user, ensuring that your Private Key is your sole asset and never falls under the control of a third party.